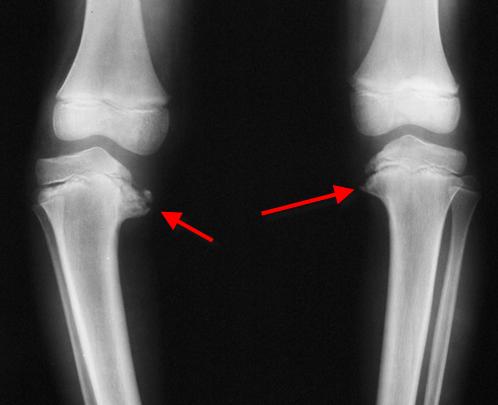
Blount’s Disease (BD) refers to a growth disorder of the shin bone (tibia) that causes the lower leg to angle inward. Although it resembles bow leg – which is common in adolescents, it is different.
Blount’s disease will not self-correct over time, but will worsen if left untreated.
Babies’ legs are naturally bowed and usually straighten out when they start walking by age 2.
Children with Blount’s disease or severe bowing before the age of 3 may be treated with knee-ankle-foot orthoses (KAFOs).
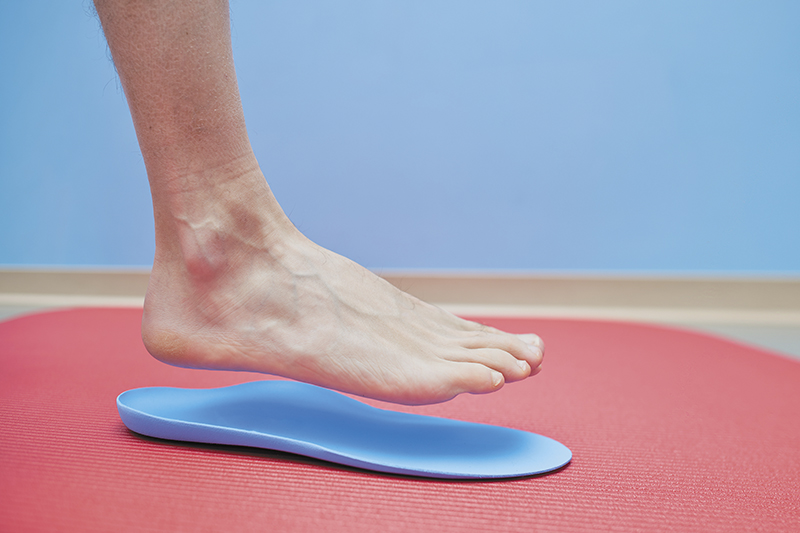

Customized in-toe gait biomechanical insoles are designed to restrict in-toeing from rotational deformities of the foot (metatarsus adductus), altering the break of the ball of the foot during propulsion to encourage realignment of the hip.
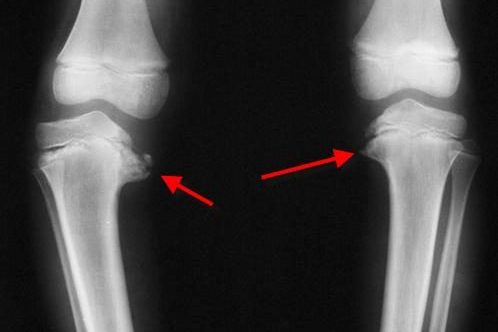
Blount’s Disease (BD) refers to a growth disorder of the shin bone (tibia) that causes the lower leg to angle inward.

It is most common in children under age two who are developing posture and balance, and may involve one or both feet.
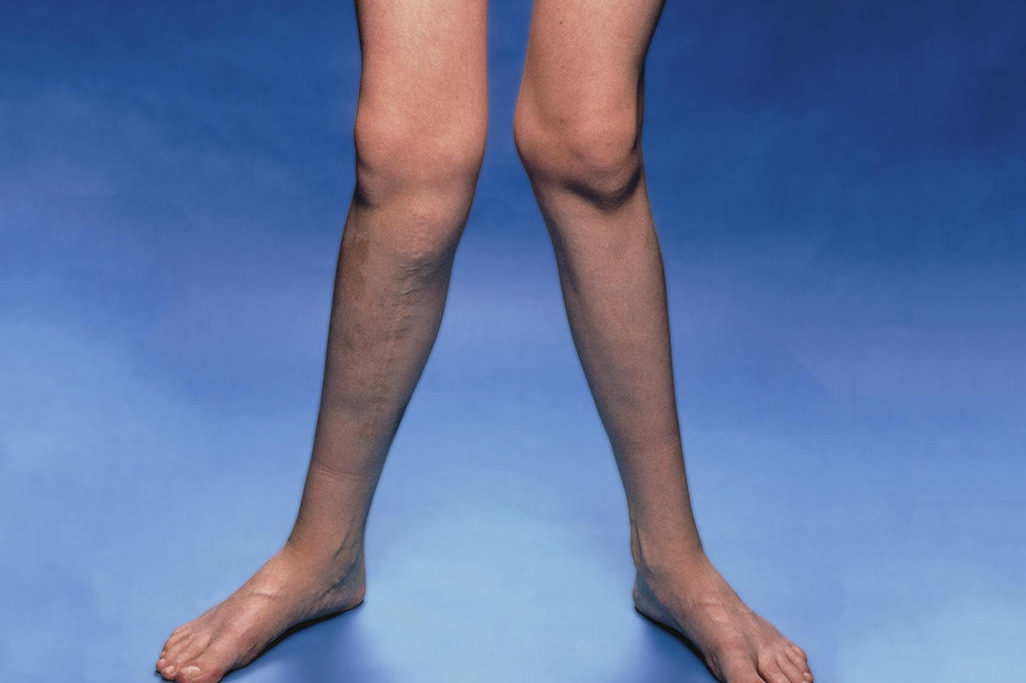
A condition where the knees angle in and touch one another when legs are stretched and straightened.

It is a type of gait abnormality in which a child loses the right contact with the ground, commonly seen in toddlers.