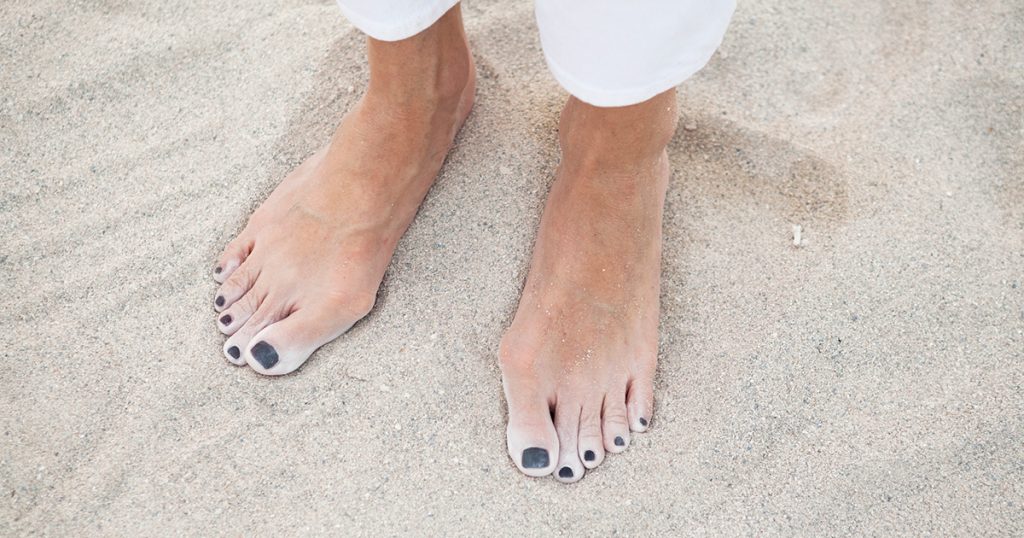

A bone deformity caused by an enlargement of the joint at the base and side of the big toe, when toes moves out of place.
Wearing shoes that are too tight is the leading cause of bunions. Bunions tend to be hereditary, but can be aggravated by shoes that are too narrow in the forefoot and toe. Though not always hereditary, they do tend to run in some families, usually due to a faulty foot structure.
As the joint flexes with each step, the bigger the bunion, the more it hurts. Foot injuries, neuromuscular problems, pronated and flat feet can contribute to their formation. Many people with bunions suffer painful discomfort from the constant irritation and friction of the enlargement against shoes.
Bunions do not self-heal as they are considered bone deformities. The aim of bunion treatment is twofold – first, to relieve the pressure and pain caused by irritations. Second, depending on the bunion size, toe misalignment and pain level, to stop any progressive growth of the enlargement.

Commonly used methods for reducing pressure and pain caused by bunions include:
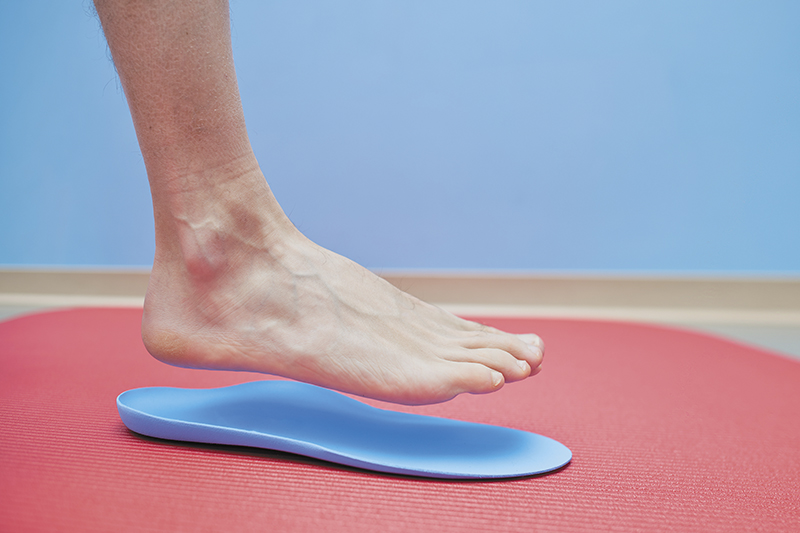

We often use two types of orthotic insoles to treat foot pain:
Our custom-made foot orthoses are prescribed and manufactured from a digital 3D foot scan taken of your feet.
Orders are sent to premium orthotic manufacturing labs in Australia or Hong Kong.
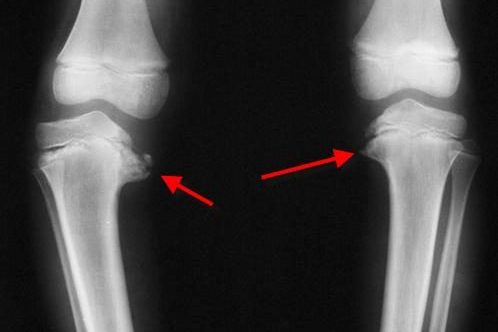
Blount’s Disease (BD) refers to a growth disorder of the shin bone (tibia) that causes the lower leg to angle inward.
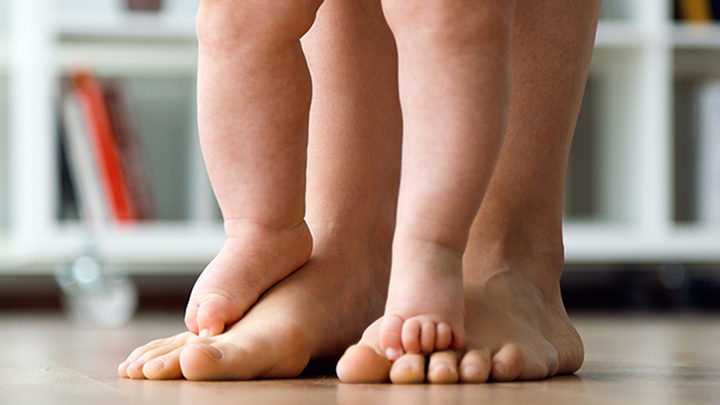

It is most common in children under age two who are developing posture and balance, and may involve one or both feet.
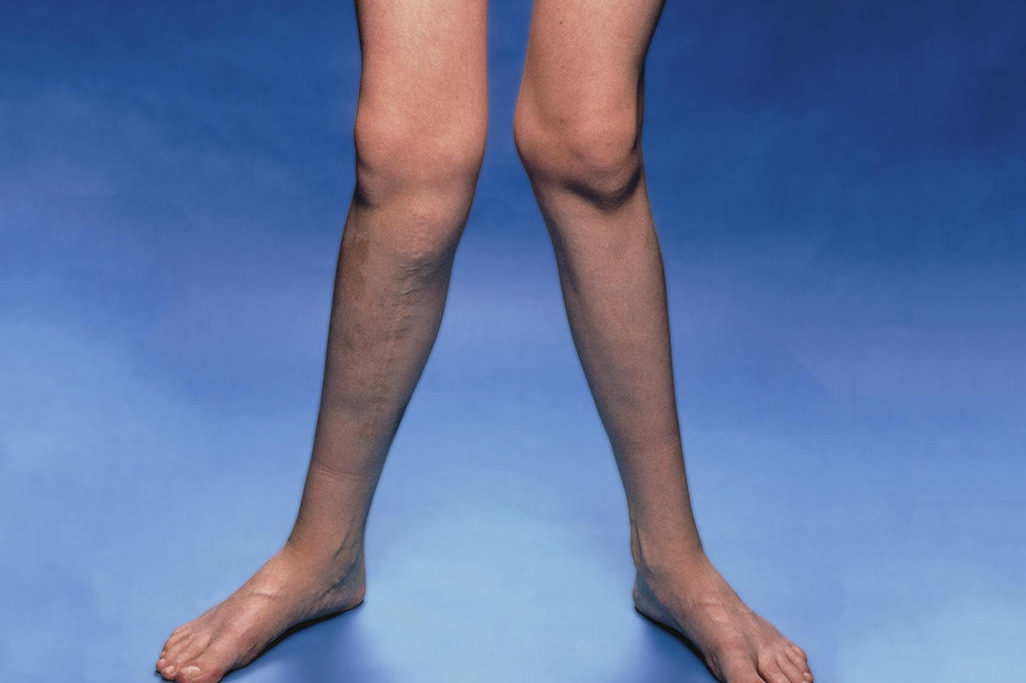
A condition where the knees angle in and touch one another when legs are stretched and straightened.

It is a type of gait abnormality in which a child loses the right contact with the ground, commonly seen in toddlers.